MyBatis源码分析
- 2022-06-27 10:33:59
- 1462次 极悦
配置解析
在Java教程中,MyBatis是学习课程之一,MyBatis 的初始化以及执行一条 SQL 语句的全流程中也包含了配置解析,我们在现实开发中一般都是使用spring boot starter的自动配置。我们一项目启动为起点一层一层剥开Mybatis的流程。先打开org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration首先明确一点就是MybatisAutoConfiguration的目的就是要得到一个SqlSessionFactory。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
Configuration configuration = this.properties.getConfiguration();
if (configuration == null && !StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
configuration = new Configuration();
}
if (configuration != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.configurationCustomizers)) {
for (ConfigurationCustomizer customizer : this.configurationCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(configuration);
}
}
factory.setConfiguration(configuration);
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
}
return factory.getObject();
}
这里是通过MybatisProperties里面的配置并放入到SqlSessionFactoryBean中,再由SqlSessionFactoryBean得到SqlSessionFactory。看到最后一行return factory.getObject();我们进去看看这个factory.getObject()的逻辑是如何得到一个SqlSessionFactory。
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
看看afterPropertiesSet()方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
重点来了,看看这个buildSqlSessionFactory()方法这里的核心目的就是将configurationProperties解析到Configuration对象中。代码太长了就不贴出来了, buildSqlSessionFactory()的逻辑我画了个图,有兴趣的小伙伴自行看一下。

Mybatis配置解析1
我们不要陷入细节之中,我们看看中点看看buildSqlSessionFactory() 方法的最后一行this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration)点进去
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
通过buildSqlSessionFactory()解析得到的Configuration对象创建一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config),到此我们就得到了SqlSessionFactory同时被配置成一个bean了。
我们最终操作都是SqlSession,什么时候会通过SqlSessionFactory得到一个SqlSession呢?
要解决这个问题我们回到最开始的MybatisAutoConfiguration的sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory)这个方法,点开SqlSessionTemplate发现它是一个实现了SqlSession到这里我们猜测就是在这里SqlSessionFactory会构建一个SqlSession出来。我们进入new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory)看看源码。
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this(sqlSessionFactory, sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getDefaultExecutorType());
}
再往下看,我们就看到了
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
这里通过动态代理创建了一个SqlSession。
参数映射、SQL解析
我们先看一下MapperFactoryBean类,这个类实现了FactoryBean在bean初始化的时候会调用getObject()方法我们看看这个类下重写的getObject()方法里的内容。
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
这里调用了sqlSession的getMapper()方法。一层一层点进去里面返回的是一个代理对象。最后的执行是由MapperProxy执行。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
接下来的流程还是画个流程图,防止小伙伴们走丢。

Mybatis参数绑定
先看一下MapperProxy中的invoke方法,cachedMapperMethod()方法将MapperMethod缓存起来了。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
我们在往下看mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args)方法。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args)这里就是处理参数转换的逻辑。还有很多细节由于篇幅有限以及时间仓促我们不做过多的赘述,感兴趣的小伙伴可以结合上面的图自己看看。下面我们看SQL的执行流程是怎么样的。整体流程如下图。
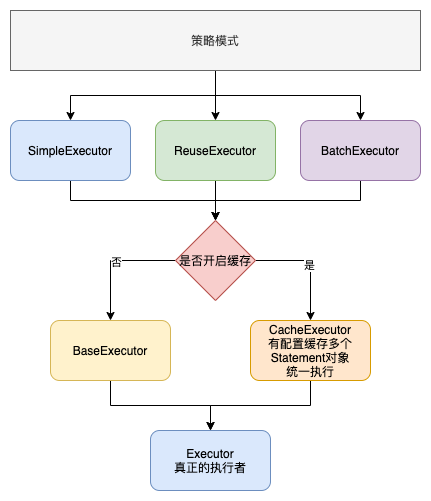
Mybatis执行流程
我们就不对每一个执行器都分析,我只挑一个SimpleExecutor来具体跟一下源码。我们还是先看看图吧,防止自己把自己搞蒙。

以simpleExecutor为例的执行流程
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
这里获取了Configuration,创建了一个StatementHandler,预处理操作,具体执行的根据创建的预处理方法,最后执行query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
statement.execute(sql);
return resultSetHandler.<E>handleResultSets(statement);
}
以上就是关于“MyBatis源码分析”的介绍,大家如果对此比较感兴趣,想了解更多相关知识,可以关注一下极悦的Mybatis视频教程,里面的课程内容由浅到深,细致全面,通俗易懂,适合小白学习,希望对大家能够有所帮助。
选你想看
你适合学Java吗?4大专业测评方法
代码逻辑 吸收能力 技术学习能力 综合素质
先测评确定适合在学习
价值1998元实验班免费学












 在线咨询
在线咨询
 免费试学
免费试学