Spring启动过程分析
- 2022-06-28 10:16:46
- 1279次 极悦
我们来看看SpringBoot启动的全过程。
1.SpringBoot的启动类是**application,注解@SpringBootApplication。
@SpringBootApplication
public class CmsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CmsApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringBoot 应用注解是@Configuration、@Enable AutoConfiguration 和@ComponentScan 注解的集成。它们代表Spring bean的配置bean,开启自动配置spring的上下文,组件扫描的路径。这就是为什么 * 应用程序。Java需要放在根路径下,所以@ComponentScan扫描就是整个项目。
其次,启动类默认只有一个main方法,调用SpringApplication。运行方法。让我们看一下 SpringApplication 类。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object source, String... args) {
return run(new Object[]{source}, args);
}
...
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
Return (new Spring Application (sources). run (args); //sources is the specific CmsApplication. class class class class
}
...
通过提取两个直接调用的run方法,可以看到静态方法SpringApplication。run 最后创建一个 SpringApplication 并在其中运行 run 方法。
查看构造方法:
public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.initialize(sources);
}
...
设置基值后调用initialize方法初始化构造函数,如下:
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
this.webEnvironment = this.deduceWebEnvironment();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
...
2.初始化方法主要做了几个步骤:
(1)将source放在SpringApplication的source属性中,source是一个LinkedHashSet(),也就是说我们可以同时创建多个自定义的非重复应用,但是目前只有一个。
(2)判断是否为web程序(?javax.servlet.Servlet且org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContextAll必须存在于类加载器中并设置为webEnvironmentAttribute.
(3)从spring中找到Application Context Initializer。工厂并将其设置为初始化程序。
(4)从spring中找到Application Listener。工厂并将其实例化为 Spring Application 的 listener listeners 属性。这个过程是找到所有的应用程序事件监听器。
(5)找出主方法类(这里是CmsApplication),返回Class对象。
默认情况下,initialize 方法从 spring 中查找键为 ApplicationContextInitializer 的类。工厂文件:
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.boot.context.web.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer
关键是ApplicationListener。
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
3.SpringApplication的构建和初始化完成后,运行run方法。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch ();// Construct a Task Execution Observer
StopWatch. start ();// Start execution, record start time
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// Get Spring Application RunListeners with only one Event Publishing RunListener inside
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
// Encapsulate Spring Application Event events and broadcast them to listeners in Spring Application to start listening
listeners.starting();
try {
// Construct an application parameter holder class
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// Load Configuration Environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// Create Spring containers (using BeanUtils. instantiate)
context = this.createApplicationContext();
// If container creation fails, analyze the cause of output failure
new FailureAnalyzers(context);
// Setting up container configuration environment, monitoring, etc.
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// Refresh containers
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// Broadcast the Application ReadyEvent event to the corresponding listener for execution
listeners.finished(context, (Throwable)null);
StopWatch. stop ();// End of execution, record execution time
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
Return context; // Return Spring container
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, listeners, (FailureAnalyzers)analyzers, var9);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
run方法的流程分析如下。该方法的几个关键步骤如下:
(1)创建应用监听Spring Application RunListeners并开始监听
(2)加载SpringBook可配置环境。如果通过 Web 容器发布,它会加载标准环境,最终继承可配置环境。类图如下。
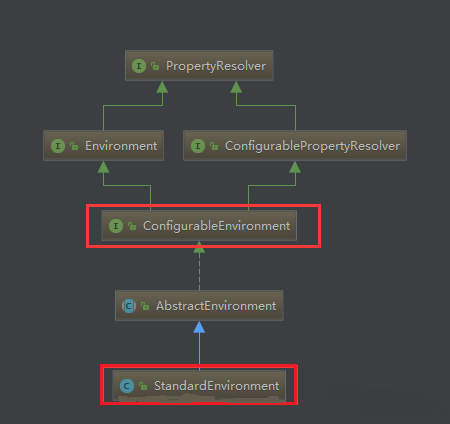
可以看到,*Environment最终实现了PropertyResolver接口,而我们通常在通过环境对象获取配置文件中Key对应的value方法时,会调用PropertyResolver接口的getProperty方法。
(3)配置环境添加到监听器对象(Spring Application RunListeners)
(4)创建Spring Container:可配置应用上下文(Application Configuration Context),我们可以看看创建方法
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment ? "org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext" : "org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}
该方法首先获取显式设置的应用上下文类,如果不存在,则加载默认环境配置(通过判断是否为web环境),默认Annotation Config应用上下文注解上下文(通过扫描所有注解类加载bean) ,最后通过BeanUtils实例化上下文对象,并返回,Configurab。leApplicationContext类图如下
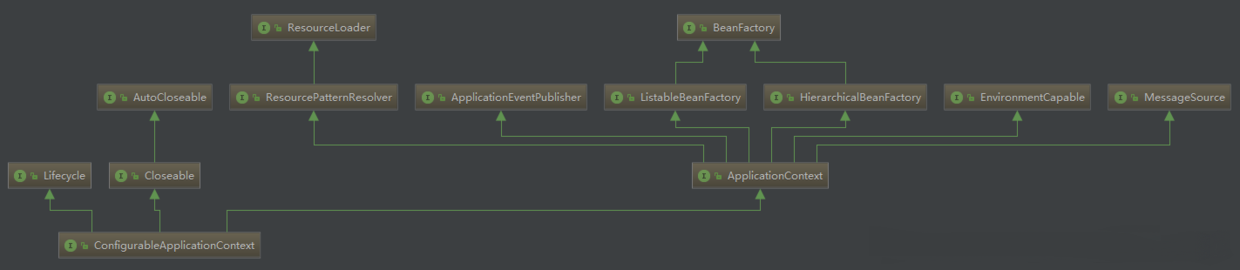
主要取决于其继承的两个方向:
LifeCycle:生命周期类,定义了start start、stop、isRunning是否运行一个中等生命周期的空值方法
ApplicationContext:应用上下文类,主要继承beanFactory类。
(5)回到run方法,设置容器prepareContext方法,将监听器、环境、应用Arguments、banner等重要组件与上下文对象关联起来。
(6)刷新容器。refresh()方法:初始化方法如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
refresh()Method做了很多核心工作,比如设置BeanFactory,执行BeanFactory PostProcessor接口,执行BeanFactory Processor接口,解析自动化配置类,加载spring。工厂,实例化bean,解析条件注释,国际化初始化等等。这部分将在以后的文章中分析。
(7)广播Application ReadyEvent并在执行结束时返回Configurable Application Context。
至此,SpringBoot启动完成,回顾一下整体流程,Springboot启动,主要创建配置环境(environment),监听器,应用上下文,根据以上条件,我们开始实例化我们需要的bean容器。如果大家想了解更多相关知识,可以关注一下极悦的Spring框架教程,里面有更丰富的知识等着大家去学习,希望对大家能够有所帮助。
选你想看
你适合学Java吗?4大专业测评方法
代码逻辑 吸收能力 技术学习能力 综合素质
先测评确定适合在学习
价值1998元实验班免费学












 在线咨询
在线咨询
 免费试学
免费试学